The pillar of well-being is thought to be sleep, which is inseparable as the food, water and air. However, to millions of individuals across the globe, sleep is being interrupted by a little known syndrome called Sleep Apnoea Syndrome. This disorder is not merely loud snoring: the effects of this health, productivity, and quality of life may be far-reaching. This article will unravel the mystery of what sleep apnoea is, why and how it occurs, how best sleeping pills uk presents itself and what can be done about it.
What Is Sleep Apnoea Syndrome?
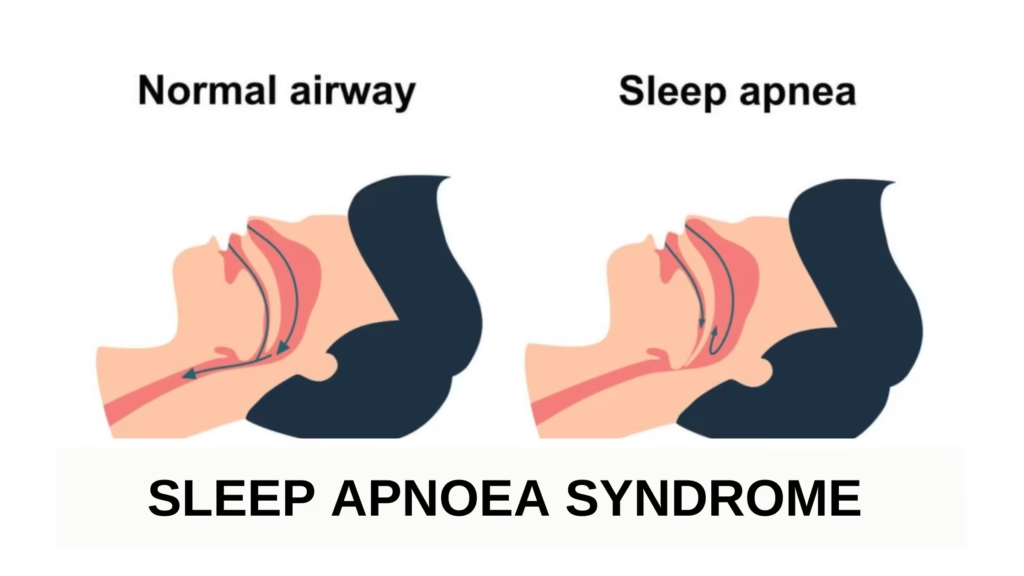
Sleep Apnoea syndrome is a sleeping disorder in which the breathing of the individual repeatedly pauses and resumes when asleep. Such breaks in breathing, which are termed ‘apnoeas‘, may last from a few seconds up to nearly a minute and may occur dozens or even hundreds of times during a night. Each interruption reduces the oxygen supply of the sleeper, and the brain reacts to this situation by briefly waking the individual enough to resume breathing.
Despite the fact that most individuals overlook loud snoring as another nuisance, when coupled with these breathing disruptions, it becomes one of the symptoms of this disease.
It consists of three known types:
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA): The most prevalent one, as a result of excessively relaxed and collapsing throat muscles, blocking airflow.
Central Sleep Apnoea (CSA): Less frequent, and in which the brain does not give the right signal to the breathing muscles even when the airway is open.
Complex Sleep Apnoea Syndrome (Mixed Type): A combination of obstructive and central forms.
Causes and Risk Factors
The cause of sleep apnoea differs according to the type. Structural and lifestyle factors are significant in the case of OSA, and CSA is typically associated with neurological or heart problems. Common risk factors include:
Obesity: The presence of excess fats near the neck and the upper airways will reduce the airways.
Age: Age is a risk factor, with prevalence rising above the age of 40.
Gender: Men are more prone compared to women, but post-menopausal women are also in the high-risk cohort.
The features of the anatomy: The individuals can be predisposed by large tonsillitis, thick neck circumference, or narrow jaw.
Alcohol, smoking and sedatives: these substances cause airway muscles to relax, increasing the likelihood of obstruction.
Medical diseases: Central apnoea is at risk with heart failure, stroke, and some neurological disorders.
Genetics: The family history may be helpful as well.
Due Signs You Can’t Disregard.
Not all victims of sleep apnoea spend the night unconscious, as the most evident symptoms occur in sleep. The signs are often spotted by a bed partner or other family member. Key symptoms include:
Snorting (usually accompanied by the sounds of choking or gasping) is loud, persistent snoring.
Breathing stops, as noted by other people when sleeping.
Daytime fatigue or sleepiness, even after a seemingly full night of rest
Oxygen deprivation during the night causes morning headaches.
Poor attention or weaknesses in memory.
Irritability, mood swings, or even depression
On waking, dry mouth or sore throat.
Without treatment, these symptoms may impair job performance, risk more accidents because of drowsy driving, and put a strain on personal relationships.
Health Consequences of Untreated Sleep Apnoea
Sleep apnoea is also more than a simple nuisance; it is a health hazard. Chronic oxygen deprivation and sleep disruption stress nearly every system of the body. However, potential complications are:
High blood pressure and heart disease: Repeated oxygen dips also put excessive pressure on the cardiovascular system.
Stroke: Constricted arteries along with an increased tendency to clot also increase the risk of stroke.
Type 2 diabetes: The insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism are subject to change due to poor sleep.
Obesity reinforcement: Obesity results in sleep deprivation, which supports hormonal disequilibriums that also cause appetite and fat buildup.
Mental health problems: Anxiety, depression and cognitive impairment may be aggravated by untreated apnoea.
Diagnosis
A sleep study (polysomnography) is frequently prescribed by physicians and is performed during the night in a sleep laboratory or at home by means of portable equipment. The test monitors:
Brain activity
Oxygen levels
Heart rate
Breathing effort
Naresalaryngeal airflow.
The severity of the disorder is determined by the Apnoea-Hypopnoea Index (AHI), which is the number of breathing pauses per hour:
Mild: 5–15 episodes/hour
Moderate: 15–30 episodes/hour
Severe: 30+ episodes/hour
Treatment Options
The degree of severity, underlying cause, and general health of the patient rely on the management. In addition, approaches include:
Lifestyle Modifications
Diet and exercise are effective means of weight loss and minimise obstruction.
Throat muscles can be made firm by avoiding alcohol, sedatives, and smoking.
Sleeping on the side instead of sleeping on the back lowers airway collapse.
Medical Devices
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): This treatment involves the use of a mask to provide sustained air pressure in order to ensure airways remain open – it is the gold standard treatment of moderate-severe OSA.
Conclusion
Sleep apnoea syndrome is not an inconvenience by far – it is a chronic condition that has far-reaching consequences for both physical and emotional health. Learning, education and early intervention can change lives, bring back vitality and avoid life-threatening complications. When you or a loved one experience a chronic case of snoring or even feel excessively tired during the day, a consultation with a doctor may be the initial move towards a healthier and more restful life.
To sleeping pills online, you can simply refer to our pharmacy. sleepingpillls one of the reliable pharmacies in the UK.